Chrome OS and Windows OS are two popular operating systems used by individuals and businesses around the world. While both operating systems have their own strengths and weaknesses, there are several key differences between Chrome OS and Windows that users should consider when deciding which one to use.
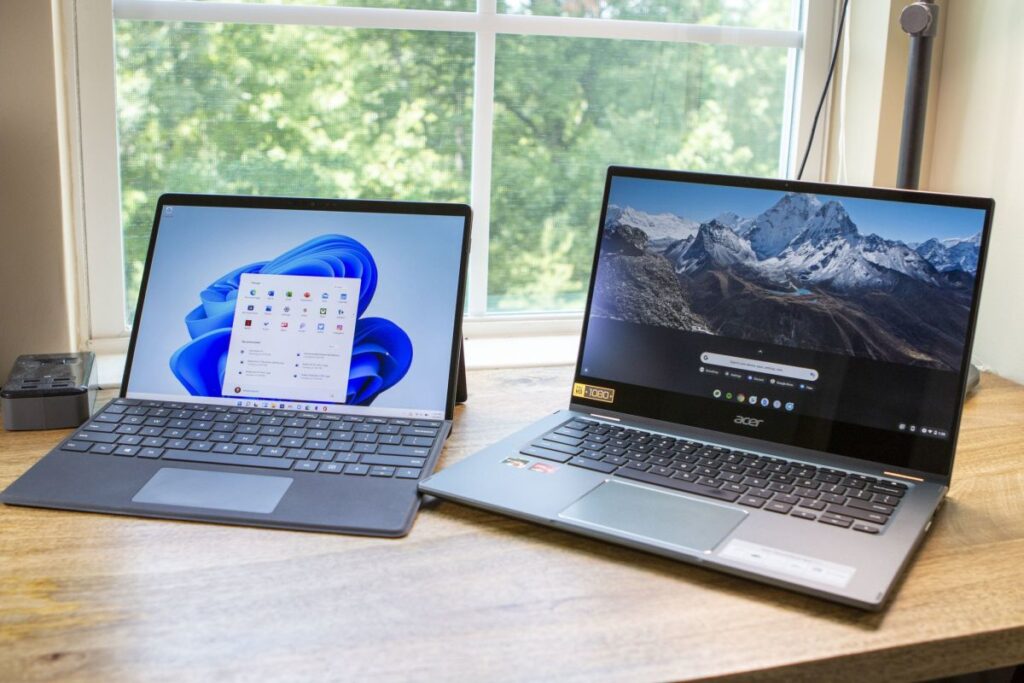

- Target Audience :- One of the primary differences between Chrome OS and Windows is their target audience. Chrome OS is designed for individuals and businesses that primarily use web-based applications and services, while Windows is designed for a broader range of users, including those who need to use locally installed applications.
- User Interface :- Another significant difference between Chrome OS and Windows is their user interface. Chrome OS has a minimalist user interface that is designed to be simple and easy to use. The operating system centers around the Chrome web browser and provides access to web-based applications and services. Windows, on the other hand, has a more complex user interface that provides access to both web-based and locally installed applications.
- Applications :- Chrome OS and Windows differ significantly in terms of the applications they support. Chrome OS is primarily designed to support web-based applications and services, and its Chrome web browser is the primary means of accessing these applications. Windows, on the other hand, supports a wide range of applications, including web-based and locally installed applications.
- Software Compatibility :- Another significant difference between Chrome OS and Windows is software compatibility. While Windows supports a wide range of software, including legacy software that may not be compatible with newer operating systems, Chrome OS only supports web-based applications and services. This means that if a user needs to run software that is not available as a web-based application, they may need to use a different operating system.
- Security :- Security is another area where Chrome OS and Windows differ significantly. Chrome OS is designed to be a highly secure operating system, with built-in features like automatic updates, sandboxed applications, and verified boot. This makes it much more difficult for malware to infect the system or for unauthorized access to occur. Windows, on the other hand, is more prone to security vulnerabilities, which can be exploited by malware and other malicious software.
- Cost :- Cost is another significant factor to consider when comparing Chrome OS and Windows. Chrome OS is generally less expensive than Windows, as it is often sold on low-cost Chromebooks. In contrast, Windows is typically sold as a standalone operating system or pre-installed on more expensive laptops and desktops.
- Hardware Compatibility :- Another area where Chrome OS and Windows differ is hardware compatibility. Chrome OS is designed to work on a limited range of hardware, primarily Chromebooks, which are designed to be affordable and easy to use. Windows, on the other hand, supports a much broader range of hardware, including desktops, laptops, and tablets.
- Customizability :- Finally, Chrome OS and Windows differ in terms of customizability. Chrome OS is designed to be a simple and easy-to-use operating system, and users have limited options for customizing the interface or adding new features. In contrast, Windows is a much more customizable operating system, and users can modify the interface and add new features using a wide range of third-party software and tools.
In conclusion, Chrome OS and Windows are two very different operating systems, each with their own strengths and weaknesses.
Chrome OS is designed for individuals and businesses that primarily use web-based applications and services and offers a simple, easy-to-use interface and high level of security.
Windows, on the other hand, is designed for a broader range of users, including those who need to use locally installed applications, and offers a more complex interface and wider range of software compatibility. Ultimately, the choice between Chrome OS and Windows will depend on the user’s specific needs and preferences.
